Raw whey protein has become a popular choice among fitness enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals due to its minimal processing and high nutritional value. But what exactly is raw whey protein, and how is it made? Let’s explore the journey from milk to this unprocessed protein powerhouse.
What Is Raw Whey Protein?
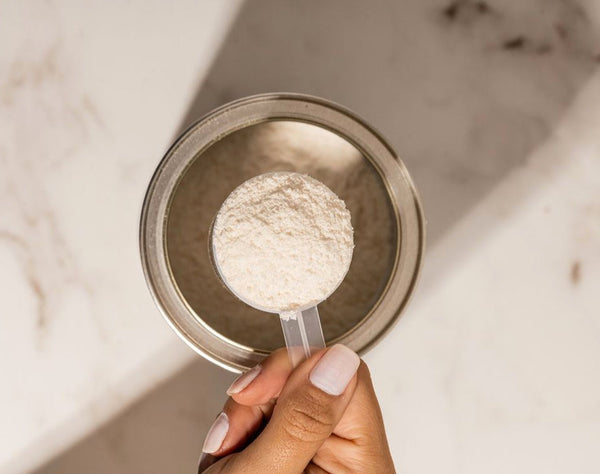
Raw whey protein is considered the purest and most natural form of whey protein available on the market. Unlike regular whey protein, which often undergoes heavy processing to remove impurities, raw whey protein is minimally processed to retain the maximum amount of its natural nutrients, enzymes, and bioactive compounds. It’s a byproduct of the cheese-making process, where milk is separated into curds and whey. After the curdling process, the liquid whey is then isolated and purified to form the protein powder. Because it’s in its raw state, this protein powder contains fewer additives, preservatives, and artificial sweeteners, offering a cleaner, more natural protein source.
This makes it an ideal choice for people who are looking to fuel their bodies with a clean source of protein that supports muscle growth, tissue repair, recovery after exercise, and overall wellness. Whether you are a fitness enthusiast, athlete, or simply someone looking to boost your protein intake in the most wholesome way possible, raw whey protein offers an exceptional way to meet your dietary needs.
How Is Raw Whey Protein Made?
-
Milk Collection: The journey of raw whey protein begins with sourcing high-quality milk from healthy cows. To ensure the best nutritional profile, many brands opt for milk from grass-fed cows, which provide a richer source of omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). Grass-fed milk tends to be more nutrient-dense, offering a better ratio of beneficial fats, vitamins, and minerals.
-
Curdling: Once the milk has been collected, it’s treated with enzymes or acids that help separate the liquid whey from the curds. The curds are typically used to make cheese, while the liquid whey contains a wealth of proteins, amino acids, and bioactive compounds. This curdling step is the crucial first part of turning regular milk into whey protein.
-
Filtration: After the curdling process, the liquid whey is then filtered through several advanced techniques to remove the majority of the fats and carbohydrates, ensuring that the protein content is concentrated. The two most common methods of filtration are:
-
Microfiltration: This process removes larger particles like fat and casein (the main protein in milk), leaving behind the whey protein in a purer form.
-
Ultrafiltration: This step further refines the liquid whey by isolating the protein even more, removing smaller particles, and increasing the protein concentration. Ultrafiltration ensures the final product is as nutrient-dense as possible without losing valuable bioactive compounds.
-
Drying: Once the whey has been filtered and concentrated, it’s spray-dried at low temperatures to form the final raw whey protein powder. The drying process is carefully controlled to ensure the protein doesn’t degrade, preserving the integrity of the natural enzymes, amino acids, and nutrients. Low-temperature drying helps maintain the delicate bioactive compounds in raw whey, which may be lost in higher heat processes.
-
Packaging: The final step is packaging. At this stage, the raw whey protein powder is free from any added sugars, artificial flavors, or preservatives. It’s a completely natural product that’s ready for use, ensuring that the consumer gets the purest form of protein available.
Benefits of Raw Whey Protein
-
High Protein Content: Raw whey protein is packed with all nine essential amino acids, the building blocks your body needs to repair and build muscle tissue. This makes it an excellent choice for athletes and anyone looking to support their muscle growth or recovery. Additionally, the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), particularly leucine, are known to promote muscle protein synthesis, further supporting recovery and muscle repair.
-
Minimal Processing: One of the key benefits of raw whey protein is its minimal processing, which helps it retain more of its natural enzymes and nutrients. These enzymes, including lactase and protease, can aid in digestion and absorption, making raw whey protein easier on the stomach compared to more heavily processed protein powders.
-
No Additives: Unlike many mass-market protein powders that are loaded with artificial sweeteners, flavors, or preservatives, raw whey protein contains none of these additives. It’s free from fillers and chemicals, making it a cleaner choice for anyone looking to avoid unnecessary ingredients.
-
Rich in Immunoglobulins: Immunoglobulins are proteins that play a key role in supporting a healthy immune system. Raw whey protein contains high levels of immunoglobulins, which can help strengthen your immune defenses and aid in overall health.
Choosing the Right Raw Whey Protein
When selecting raw whey protein, it’s important to consider the following:
-
Source: The quality of the milk used to make the protein is essential. Grass-fed, hormone-free cows are typically a better source for higher quality protein powder.
-
Processing Method: Look for raw whey protein that’s been processed using low temperatures. This helps preserve the vital nutrients that are often lost during high-temperature processing.
-
Certifications: Ensure that the product is certified free from contaminants and impurities. Look for certifications like non-GMO, gluten-free, and third-party testing to ensure you’re getting a high-quality product.
How to Use Raw Whey Protein
-
Post-Workout Shake: The most common use for raw whey protein is in a post-workout shake. After intense exercise, your muscles need protein to recover and repair. Mixing raw whey protein with water or milk gives your body the essential nutrients it needs to restore muscle fibers and kickstart the recovery process.
-
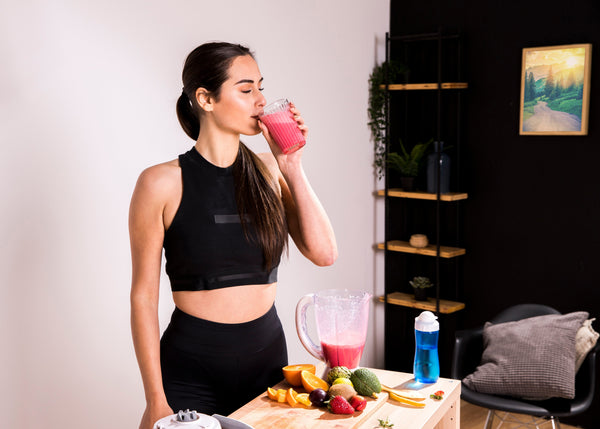
Smoothies: If you’re looking to create a more well-rounded snack or meal, blend raw whey protein into a smoothie with your favorite fruits, vegetables, and other superfoods. This way, you can increase your protein intake while also adding vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to your diet.
-
Baking: Raw whey protein isn’t just for shakes and smoothies; you can also incorporate it into your baking recipes. Add it to pancake or muffin batter for a delicious, protein-packed breakfast or snack. This is a great way to get your protein in without sacrificing taste.
Whether you’re an athlete, bodybuilder, or simply someone looking to boost your daily protein intake, raw whey protein provides a clean, high-quality option for reaching your nutritional goals. Its minimal processing ensures you’re getting a product that’s as close to its natural form as possible, making it an excellent addition to any health-conscious diet.